A new interesting technique of ransom attached to a rapidly spreading ransomware attack in China is getting the world’s tech leaders attention as the infection has spread to more than 100,000 computers in the last four days as a result of a supply-chain attack. An impactful point is that the number of infected users is continuously growing every hour.
This particular ransomware is unlike WannaCry and NotPetya, the worlds largest ransomware outbreaks that caused worldwide chaos last year, this new Chinese ransomware has been targeting only Chinese users so far and unlike the other two, this new virus doesn’t demand ransom payments in Bitcoin.
Instead, that attackers behind this are asking victims to pay 110yuan (nearly 16USD) in ransom through WeChat Pay – the payment system that is featured within China’s most popular messaging app.
Ransomware + PAssword Stealer – This Ransomware also includes an additional ability to steal users’ account passwords for Alipay, Taobao, Tmall, NetEase 163, Baidu Cloud Disk, JingJong, AliWW, and QQ websites.
How does this move so fast?
According to Chinse Cybersecurity and anti-virus firm
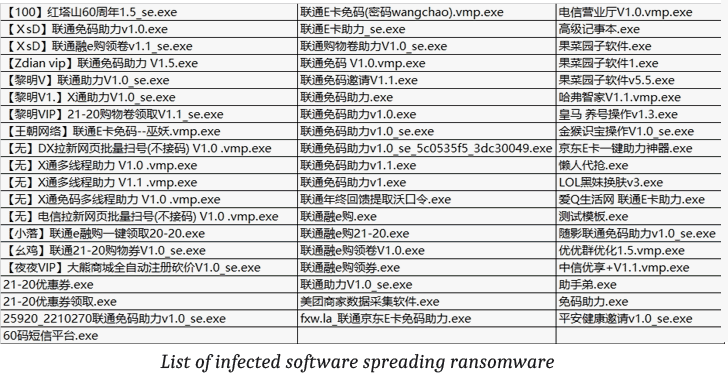
Velvet Security, attackers added malicious code into the EasyLAnguage” programming software used by a large number of application developers. The malicious programming software was built and designed to inject ransomware code into every application and software product compiled through it – another example of a software supply-chain attack to spread the virus rapidly.
Anyone that went ahead and installed any of the above listed infected applications got their systems compromised. This ransomware encrypts all files on the infected user’s system, except files with gif, exe, and tmp extensions.
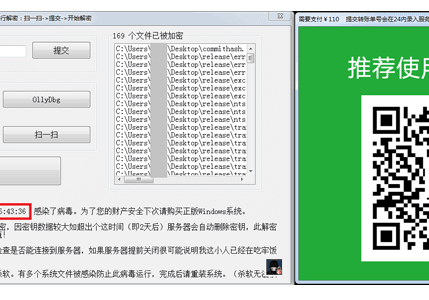
Once encrypted, the ransomware pops-up a note, asking users to pay 110 yuan to attackers’ WeChat account within 3 days to receive the decryption key.
If the vulnerable users do not pay the ransom amount within the specified time, the hackers (through the malware) threaten to delete the decryption key from its remote command-and-control server automatically and it also quietly steals users login credential from popular Chinese websites and social media accounts and sends them to a remote server.
Not only that this ransomware also gat5hers system information including CPU model, screen resolution, network information and list of installed software.
The Hackers have left a note that tells users that their files have been encrypted using DES encryption algorithm, but in reality, it encrypts data using a less secure XOR cipher and stores a copy of the decryption key locally on the victim’s system itself in a folder at the following location:
%user%\AppData\Roaming\unname_1989\dataFile\appCfg.cfg
The Velvet Security team created and released a
free ransomware decryption tool that can easily unlock encrypted files for victims without requiring them to pay any ransom. The researchers of the security firm were also able to crack and access attackers’ command-and-control and their MySQL database servers and found thousands of stolen credentials stored on them.
Who’s behind these attacks?
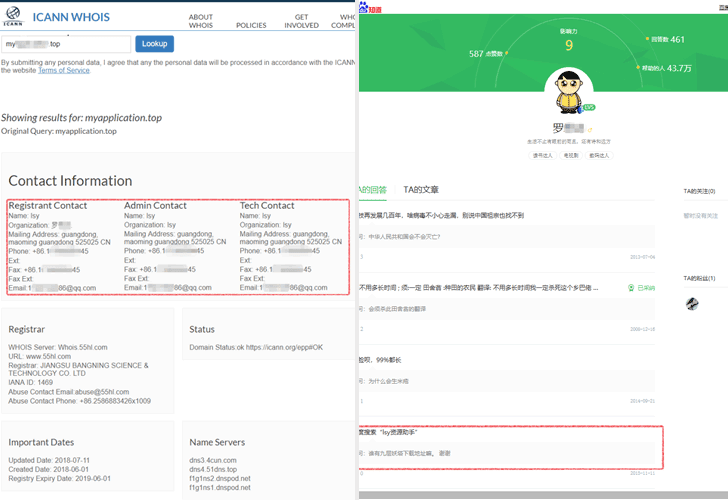
Security researchers have found a suspect, named “Luo”, using publicly available information. Luo, who is a software programmer by profession and developed applications like “Isy resource assistant” and “LSY classic alarm v1.1”
According to researchers, Lua’s QQ account number, mobile number, Alipay ID and email IDs match with the information researchers collected by following the attacker’s WeChat account.
WeChat has no suspended the attackers account on its service that was being used to receive the ransom payments.
It has been reported that this Ransomware was set to make movements aboard with its first western location being Australia which is the closest to China. Tech Patrol stays on top of ALL international ransomware attacks and always keep our clients secure. If you have any further questions regarding this article please
email me.

















Share your thoughts in the Comments section: